Virtualization -
Virtualization is a technology that allows the creation of virtual environments to perform tasks that would typically run on physical computer hardware. It involves the creation of virtual machines, servers, and other resources that mimic the behavior of real physical machines.
Types of Virtualizations
There are five main types of virtualizations:
- Operating System Virtualization: This involves hosting multiple operating systems on a single local operating system. The technology got its start on mainframes decades ago by allowing administrators to avoid wasting a lot of money and expensive processing power. Linux-VServer, Parallels Virtuozzo Containers, OpenVZ, and Solaris Containers are examples of operating system virtualization.
- Application Virtualization: In Application Virtualization, independent applications are hosted in a virtual environment separate from the local operating system. Itallows users to use and access an application from a separate computer rather than where it is installed. Virtualizing Microsoft PowerPoint to run on Ubuntu over any browser is an example of application virtualization.
- Service Virtualization: In this, specific processes and services related to a particular application are hosted in a virtual environment. It provides teams with easy access to the constrained components that impede development and testing.It helps to improve server reliability and availability.
- Network Virtualization: In this type of virtualization, multiple virtual networks can be executed, each with its own control and data plan. It can combine multiple physical networks into one virtual, software-based network, or it can divide one physical network into separate, independent virtual networks. It helps organizations to achieve major advances in speed, agility, and security.
- Server Virtualization: This type of virtualization involves masking server resources to create virtual servers. Server virtualization is a cost-effective way to provide web hosting services and effectively utilize existing resources in IT infrastructure. There are three main types of server virtualization: full virtualization, para-virtualization, and OS-level virtualization.

Exploring VMware: Innovating Virtualization and Cloud Computing
VMware is an American company specializing in virtualization technology and cloud computing. It was established in 1998 and later became part of Dell Technologies. VMware provides multi-cloud solutions for various applications, enabling digital progress while maintaining enterprise governance.
The core of VMware's virtualization technologies is its bare-metal hypervisor ESX/ESXi, which is based on x86 architecture. This hypervisor software allows the creation and operation of virtual machines on a single physical server.
Benefits of VMware's virtualization technology:

Saving of Cost: Organizations can save costs by consolidating servers and optimizing hardware utilization, reducing power consumption, cooling, and maintenance expenses.

Improved Resource Utilization: Virtualization allows for dynamic allocation of computing resources based on demand, leading to better overall system performance and efficiency.

Scalability and Flexibility: Organizations can easily scale their IT infrastructure up or down as needed, offering flexibility in meeting the changing demands. Scalability and flexibility in IT infrastructure empower organizations to adapt rapidly to varying workloads and operational needs.

Better Security: VMware's virtualization technology enhances security by isolating applications and data within virtual machines, making it easier to implement security features like virtual firewalls and intrusion detection systems.

Easy Management: VMware provides centralized management tools that simplify the administration and monitoring of virtualized environments, reducing complexity in managing large-scale infrastructures.
Hypervisors: Your Virtual Machine Managers
Hypervisor is a software that helps us to create and manage virtual machines. It is also known as a Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM). The hypervisor runs on a host machine, and each virtual machine it manages is called a guest machine.
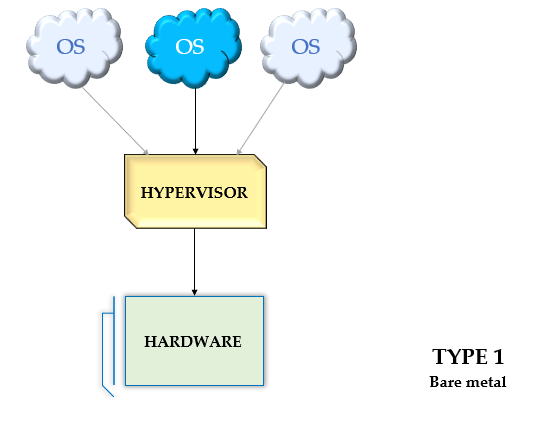
There are two main types of hypervisors:
- Type 1 Hypervisor: These types of hypervisors are also known as bare-metal hypervisors. They directly run on hardware without any operating system. Examples include VMware ESXi, Citrix XenServer, and Microsoft Hyper-V.
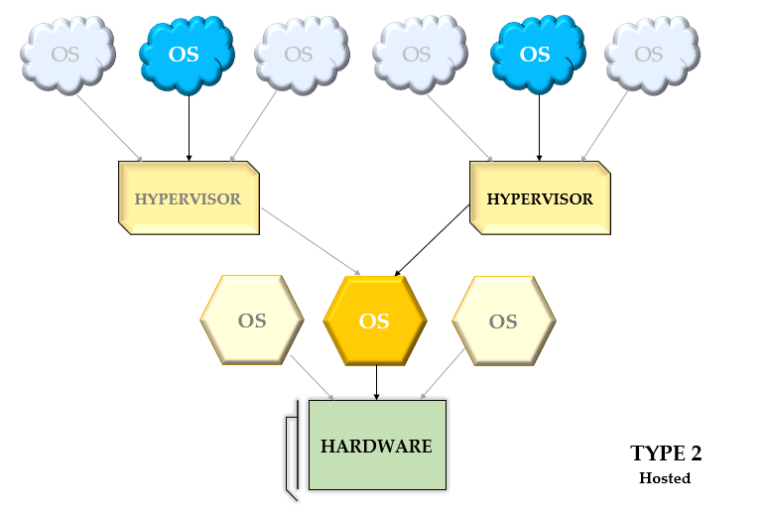
- Type 2 Hypervisor: This type of hypervisor is also known as hosted hypervisor. These hypervisors are deployed as software applications on an existing operating system. Examples include VMware Workstation, VMware Fusion, and Oracle VirtualBox.
Benefits of using a Hypervisor:
- Server Consolidation: Hypervisors allow multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server, maximizing hardware utilization and reducing the need for multiple physical machines.
- Snapshot and Rollback: Hypervisors enable the creation of snapshots, capturing the state of a virtual machine at a specific moment, useful for backups, testing, or rolling back to a previous stable state.
- High Availability and Fault Tolerance: Advanced hypervisors offer features like clustering and live migration, ensuring high availability and minimal downtime in case of hardware failures.
- Testing and Development: Virtual machines are excellent for testing and development purposes, as they provide isolated environments for trying out new software without affecting the production system.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, virtualization technology, represented by VMware and various hypervisors, has revolutionized IT infrastructure, offering cost savings, improved resource utilization, and enhanced security. It provides scalability, flexibility, and easy management for organizations to meet changing demands. Hypervisors enable server consolidation, testing, and development while ensuring high availability and fault tolerance. Embracing virtualization has become a fundamental strategy for modern businesses, driving digital progress and optimizing IT investments.
By Dheeraj Sain
Project Engineer