ITIL Basics: Your Introduction to IT Service Management
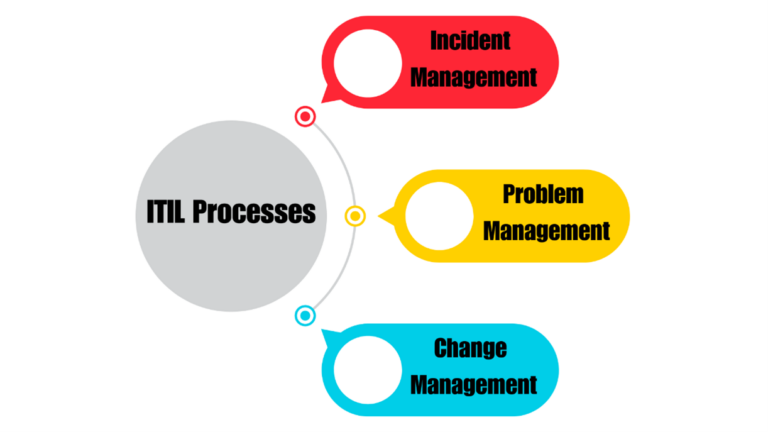
The Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is a set of best practices for IT service management designed to help organizations manage risk, improve customer relations, establish cost-effective practices, and build a stable IT environment. In service management, ITIL processes are essential for ensuring efficient and effective project delivery. This blog delves into the key ITIL processes involved in service management: Incident Management, Problem Management, and Change Management. We will also provide practical examples to help you better understand these concepts.

Key ITIL processes in service management are as follows:
Incident Management
Incident Management is the process of managing deviations from the expected standard of IT service. It involves identifying and resolving incidents to restore normal service operation as quickly as possible, minimizing the impact on business operations.
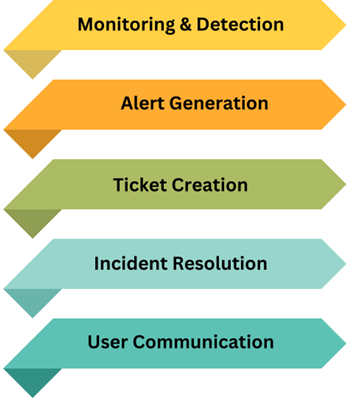
Steps in Incident Management
- Monitoring and Detection: Continuous monitoring of IT services is essential to detect any deviations or incidents. Tools like Nagios, Zabbix, Prometheus, Kibana, Grafana, etc help in real-time monitoring and alert generation.
- Alert Generation: When an incident is detected, alerts are generated to notify the IT team. These alerts can be sent via email, SMS, or through integrated systems.
- Ticket Creation: Once an alert is generated, a ticket is created in a ticketing tool such as ServiceNow, Jira, or Zendesk. This ticket contains details about the incident and is assigned to the appropriate team for resolution. The system can also prioritize incidents based on severity.
- Incident Resolution: The IT team works on resolving the incident. The progress is tracked in the ticketing tool, and updates are provided until the incident is resolved.
- User Communication: Throughout the incident management process, users are kept informed about the status and expected resolution time. Communication can be via email, phone calls, or through the ticketing system.
Example
Imagine a company’s email server storage utilisation has reached 90%. Monitoring tools like Nagios detect this outage and generate an alert. This alert triggers the creation of a ticket in ServiceNow. The IT team receives the ticket, diagnoses the issue, and brought down the storage utilisation under threshold values to resolve the issue. After the issue is resolved, the ticket gets closed and the affected users are notified.
Problem Management
Problem Management aims to identify and eliminate the root causes of incidents to prevent them from recurring. This process involves creating and managing problem tickets.
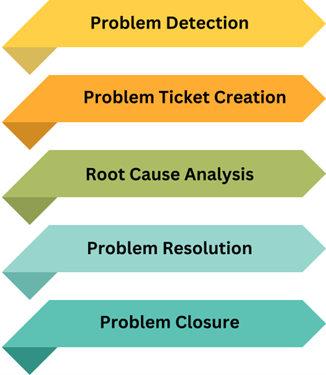
Steps in Problem Management
- Problem Detection: Problems are identified either through recurring incidents or proactive analysis. Tools like Kibana, Grafana, etc. help in analyzing incident trends and identifying potential problems.
- Problem Ticket Creation: Once a problem is identified, a problem ticket is created in tools like ServiceNow or Jira. This ticket contains detailed information about the problem, its impact, and potential root causes.
- Root Cause Analysis: The IT team conducts a thorough analysis to identify the root cause of the problem. Techniques like the 5 Whys or Fishbone Diagram can be used for this analysis.
- Problem Resolution: Solutions are developed and implemented to eliminate the root cause. This may involve changes to the IT infrastructure, processes, or policies.
- Problem Closure: Once the problem is resolved and verified, the problem ticket is closed. Documentation is updated to reflect the changes made and lessons learned.
Example
A company experiences frequent network outages. The IT team uses Kibana to analyze the incidents and identifies a pattern suggesting a faulty router as the root cause. A problem ticket is created in ServiceNow, and the team replaces the faulty router, resolving the issue. The documentation is updated with this information to prevent similar future occurrences.
Change Management
Change Management ensures that all changes to the IT environment are managed in a controlled and systematic manner. This process helps minimize the risk of disruption and ensures that changes are beneficial.
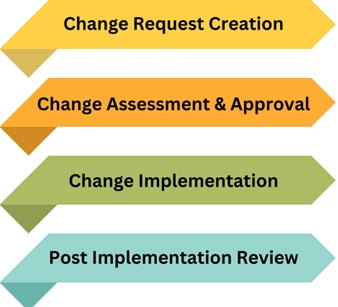
Steps in Change Management
- Change Request Creation: When a change is needed, a change request is created in tools like ServiceNow or BMC Remedy. This request includes details about the change, its impact, and the plan for implementation.
- Change Assessment and Approval: The change request is reviewed by a Change Advisory Board (CAB), which assesses the risk, impact, and benefits of the change. The CAB includes representatives from different stakeholders to ensure a comprehensive evaluation.
- Change Implementation: Once approved, the change is scheduled and implemented according to the plan. This may involve a “Change Freeze” period, during which no changes are made to the environment to ensure stability.
- Post-Implementation Review: After the change is implemented, a review is conducted to ensure that it was successful and did not cause any unintended issues. The change request is then closed.
Example
A company needs to upgrade its database server to improve performance. A change request is created in ServiceNow detailing the upgrade plan and potential impacts. The CAB reviews and approves the request, scheduling the change during a maintenance window. During the implementation, a “Change Freeze” is observed to prevent other changes that might interfere. After successful implementation, a review confirms the upgrade was successful, and the change request is closed.
Conclusion
ITIL process management is crucial for the effective management of IT services. By following best practices in Incident Management, Problem Management, and Change Management, organizations can ensure stable and reliable IT services. Using the right toolsets for monitoring, alerting, ticketing solutions, etc. helps streamline these processes and enhance overall efficiency. Understanding and implementing these ITIL processes will enable your organization to manage IT services more effectively, reduce risks, and improve service quality. Continuous improvement and feedback are essential to adapting and enhancing these processes over time, aligning with long-term strategic goals.
By: Amanpreet Singh Bhogal