Data Engineer vs. Data Scientist:
Both data engineers and data scientists, in this data-driven world, stand as vital persons involved in decision-making processes. Though their roles intersect in several points, each job has a different set of responsibilities. We should look at how a data engineer and a data scientist differ from one another, as well as how they complement each other, so we understand that both are vital for modern data ecosystems.
The Role of a Data Engineer
Data engineers are, in effect, the architects of data systems. They design the infrastructure that enables data flow efficiently across an organization. Their main objective is to ensure reliability, accuracy, and availability of data for downstream applications.
Key Responsibilities
 Data Pipeline Development: Data engineers develop automated pipelines that can collect, transform, and store large amounts of data. This way, multiple sources can have their raw data converted to some usable format to enable analysis.
Data Pipeline Development: Data engineers develop automated pipelines that can collect, transform, and store large amounts of data. This way, multiple sources can have their raw data converted to some usable format to enable analysis.- Data Warehousing: In most instances, they manage the solutions used in data storage, such as data lakes or data warehouses, holding enormous sets of data.
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) Processes: Data engineers develop ETL processes to clean and transform raw data into a structured form suitable for analysis.
- Performance Optimization: Data systems are optimized to run smoothly and efficiently, so data engineers also monitor the performance of the data pipeline and storage solutions.
Essentially, the data engineers make the base of the work of a data scientist by preparation and setting high-quality and well-arranged data ready for analysis. Data scientists would really face an uphill battle to obtain and manage such large datasets without data engineers.
The Role of a Data Scientist
After preparing the data, data scientists work on the analysis and insights extraction process. By using mathematical models, statistical methods, and even machine learning algorithms, they identify trends, predict the future, and solve complex business problems.
Key Responsibilities
 Data Exploration and Analytical work: Data scientists navigate through extensive datasets for trend identification, correlation, and insights which might be helpful for making decisions.
Data Exploration and Analytical work: Data scientists navigate through extensive datasets for trend identification, correlation, and insights which might be helpful for making decisions.- Model Building: They build machine learning models in order to make predictions or recommendations automatically. For example, data scientist might create a recommendation engine or a fraud detection model.
- Experimentation and Hypothesis Testing: Data scientists often do experiments using statistical methods in order to establish hypotheses and ensuring that their findings are robust.
- Communication of Results: Data scientists translate technical results into actionable insights for business stakeholders through visualizations, dashboards, and reports.
Thus, the accuracy of their analysis and model depends on what they receive from data engineers. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to wrong conclusions, so the role of the data engineer is equally important.
Key Differences Between Data Engineers and Data Scientists
While both roles focus on data, their objectives and skill sets differ significantly.
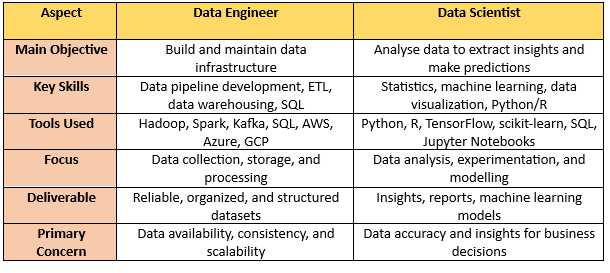
How Data Engineers and Data Scientists Work Together
Data engineers and data scientists are complementary to a great extent despite all the differences. A data engineer sets up the underlying data infrastructure so that it is both scalable, fast, and secure. Then, when the data is processed and available, it is a data scientist’s turn, applying what could be learned from it to answer critical business questions through analysis or even machine learning.
For instance, let’s consider the scenario of a retail company that is looking forward to upgrading its customer recommendation system.
- Data engineers would construct and control pipelines that aggregated customer’s browsing data, purchase history, and interaction logs from disparate sources, and further store them efficiently in a data warehouse.
- Data scientists will then use that data to train a recommendation model to recommend products from the list according to the customer’s choice.
Without proper, consistent data coming in from the engineers, the work of the data scientist would be much less effective.
Conclusion
Data engineers and data scientists play absolutely critical roles in leveraging business assets. While a good data engineer tends to focus on creating a strong data infrastructure, the data scientist stresses on the extraction of meaningful insights from that data. Work from both aspects ensures the proper efficiency and accuracy of data-driven decisions for better business outcomes.
In short, data engineers prepare the data so that it is ready to be used, while data scientists make the data useful for business purposes. Both skills are necessary to be successful in a data-driven environment today.
By – Amanpreet Singh Bhogal